Body fat (known as adipose tissue) helps your body to store energy and regulate temperature. Having too much or too little fat can both be unhealthy.
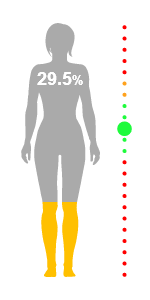
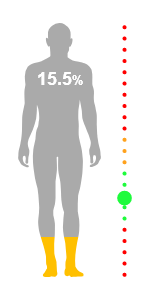
FitQuest estimates the amount of fat in your body by passing a small electrical signal through your body; a technology known as Bio Impedance Analysis (BIA). This estimate can be used to help you track your fat levels and maintain a healthy balance.
FitQuest illustrates your fat level visually on a male or female silhouette. The level of fat rises up from the bottom to illustrate the percentage of your total body mass that comprises of fat. The value is also shown numerically. A toggle allows you to view this value in relative (percentage) or absolute (kilogram) terms.
Alongside the silhouette is a gradated gauge of pips - with colours indicating varying classifications of fat levels; from too little fat (red - bottom), a healthy amount (green), too much fat (yellow) and obese (red - top). The positions of these gradations is tailored in your report according to your age and gender (see below). A larger pip indicates the classification of your current measurement.
Diet
The best advice is to maintain a healthy weight through a combination of a balanced diet, healthy eating and regular exercise.
A small amount of fat is an essential part of a healthy, balanced diet. Fat is a source of essential fatty acids (which the body can't make itself) and helps the body absorb vitamins A, D and E (which are fat-soluble and can only be absorbed with the help of fats).
Too much fat in your diet, especially saturated fats, can raise your cholesterol levels increasing your risk of heart disease. Consuming high amounts of energy, particularly fat and sugars, without burning off the energy through exercise and physical activity, leads to the body storing the surplus as body fat. So your calorie intake needs to be matched to your activity levels.
Excess consumption over time can lead to obesity which increases your risk of several potentially life-threatening conditions, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease, some cancers and strokes along with other problems linked to obesity.
Current UK government guidelines advise cutting down on all fats and replacing saturated fat with some unsaturated fat.
Its also important to perform regular exercise to maintain muscle bulk and good cardiovascular function.
Fat Classification - Typical Ranges
The charts below outline the classification of varying levels of fat - upon which the pip gradations are based.
The green banded zone indicates the range considered to be a healthy percentage of fat for typical individuals.
Note that these levels vary by age and gender (women typically carry higher levels of fat) - so be sure to reference the appropriate chart and age.
Resources
A collection of useful external resources is provided below:
- NHS - Eat Well Guide
- NHS - Fat - The Facts
- Change4life
- NHS - Eating Disorders
- BEAT - Beat Eating Disorders
- NHS - Obesity
- NHS - BMI Calculator
Disclaimer
Always seek professional and medical advice before undertaking any changes to your fitness regime, training or diet. The information we provide (in our results, applications and reports for example) is intended as a guide only (not a clinical assessment). Targets are based on averages for individuals matching your age range and gender. You should always discuss personalised targets with your doctor, trainer and dietician.
